What DevOps is not?
DevOps is not a “Packaged Solution”. I.e. You cannot buy and install it.

What is DevOps?
“DevOps is the union of people, process, and products to enable continuous delivery of value to our end users.” – Donovan Brown, MSFT
DevOps is a “culture”, where development, test, and operations work together in a collaborative manner to automate delivery of quality software. DevOps culture develops “production-first mindset”. I.e. applying DevOps ensures that your code is always ready to be deployed to production.

Why DevOps?
First thing DevOps offers is that, it breaks the “Wall of Confusion” between development and operations team. These two teams have different agenda and expectations when it comes to software delivery and deployment.

DevOps breaks the wall of confusion between teams and fosters better communication and collaboration throughout the application development lifecycle and results into better visibility and small frequent deployments together.
DevOps Benefits and ROI – Source, Forrester Research Inc.
- Improved IT operations efficiency. Saving 50% of allocated IT operations support.
- Improved developer productivity with faster, automated release processes. Developers saw a 15% improvement in productivity.
- Improved tester productivity with faster, automated release processes. 20% productivity gain with their deployment of the Microsoft DevOps solution.
- Faster recovery from failures and reduction in release risk. Reduce time-to-resolution per incident by 2 hours.
- Reduced cycle time by as much as 99% and more frequent deployments. Increased customer satisfaction and also gained new business.
- Faster speed-to-market for new features, products, and services for customers. 20x more, leading to increased sales.
- Improved release quality. Successful releases with a reduction in errors increase in release reliability, and less time on remediation of release errors.
How to apply DevOps?
Prime objective of DevOps is to “quickly ship the highest quality software to the end customers”. To make this happen DevOps needs to be implemented across all the phases of software development and delivery.
DevOps workflow from planning to release
The workflow model below shows how teams go through four phases and contribute towards DevOps adoption.
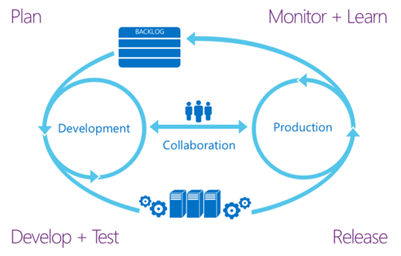
Plan – Backlog represents well-defined and prioritized user stories with proper acceptance criteria etc.
Develop & Test – Development will include good quality code written, debugged, code reviewed, checked-in including unit test coverage as appropriate. Testing will include verifying the user story’s acceptance criteria, possibly followed by performance and integration tests etc.
Release – Whenever a new version is ready and a sprint end, an automated process is used for deployment.
Monitor and Learn – After release team can gather information related to how customers use the application /services and continue to monitor health of application.
Collaboration – Building code and running unit tests on each check-in small or big ensures that code is ready to be deployed. Then, deploying it to at-least production like environment and successfully performing tests there ensures that Dev and Production are in collaboration.
DevOps Automation
One major key aspect of DevOps is automation of software build, test, and deploy. DevOps automation enables continuous value delivery. Let’s see the DevOps Automation process workflow.
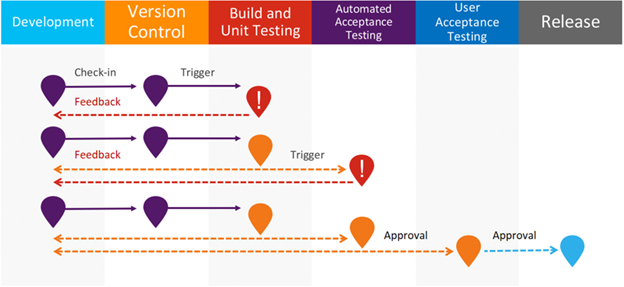
Development – This is where a developer writes code in their local development environment.
Version Control – This is version control team uses to check-in code to the repository. E.g. Git, TFS, SVN etc.
Build and Unit Testing – This is where DevOps Continuous Integration (CI) takes place. At this step, code will build with latest checked-in code and latest packages and dependencies as applicable. If there are unit tests then all unit tests will be executed to ensure that there are no collateral damages caused within the code base.
If Build fails then a notification will be sent to the developer who submitted the build. Many teams have various policies and channels set up for this. For example, a bug is created with details when a build fails and team’s slack channel will receive notification when a build fails.
Automated Acceptance Testing – If build succeeds then a set of acceptance tests can be executed automatically to verify that code is working fine.
Any failure in an acceptance test will trigger a feedback initiated to the team and process will again start from beginning.
User Acceptance Test – Passed automated acceptance tests ensures and triggers the code to be promoted to UAT.
Release – Upon passing UAT, code can be released to any environment or production or production like environment. Manual push of code to production is known as Continuous Delivery (CD).
DevOps Toolchain
DevOps is technology agnostic and any development environment on any platform can fully adopt DevOps culture and can continuously deliver quality software to their customers. Here some SDLC phases and tools which will fit in and can help to setup end-to-end DevOps pipeline for your technology and platform of choice.
Planning and Analysis
- Capturing and tracking (TFS, VSTS, JIRA, ServiceNow.
- Documentation or Wiki page (Microsoft Teams, SharePoint, Confluence.
- Collaboration (Slack, HipChat, Microsoft Teams).
Design and Development
- SCM (TFS, VSTS, Subversion, Git, Mercurial.
- IDE (Eclipse, IntelliJ, Visual Studio).
Build and Release (CI/CD)
- Repository management (Artifactory, Nuget, Nexus).
- Build tools (MSBuild, Jenkins, Bamboo).
- Configuration management (Chef, Puppet, Ansible).
- Cloud (AWS, Azure,OpenStack).
- Containers (Docker).
Integration and Testing
- Source code verification (SonarQube).
- Security testing (HP Fortify).
- Functional testing (MSTest, NUnit, JUnit, Cucumber, Selenium).
- Performance testing (SOASTA, Apache Test Bench, Microsoft Load and Performance Test).









 I am a hands-on architect with proven 19+ years of experience in architecting, designing, and developing distributed software solutions for large enterprises. At Microsoft, as a Principal Software Engineering Manager, I own the Platform team. I see software development as a craft, and I am a big proponent of software architecture and clean code discipline-n-practices. I like to see the bigger picture and make a broader impact. I was also a Microsoft MVP for past 7 years on Visual Studio and Dev Technologies I can be reached at vidya_mct@yahoo.com or twitter @dotnetauthor
I am a hands-on architect with proven 19+ years of experience in architecting, designing, and developing distributed software solutions for large enterprises. At Microsoft, as a Principal Software Engineering Manager, I own the Platform team. I see software development as a craft, and I am a big proponent of software architecture and clean code discipline-n-practices. I like to see the bigger picture and make a broader impact. I was also a Microsoft MVP for past 7 years on Visual Studio and Dev Technologies I can be reached at vidya_mct@yahoo.com or twitter @dotnetauthor



